Open topic with navigation
What is My Computer's MAC Address?
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique hardware identifier for your specific computer. The MAC address is not the same as your computer's Host ID. While connected to a network, a lookup table relates your MAC address, also known as the Physical Address, to your IP (Internet Protocol) address. You will need your computer's MAC address in order to purchase a network-based "floating" license from Keysight.
To determine your MAC (physical) address, you can use either the Windows Control Panel or the Windows Command Prompt.
From Windows Control Panel
- Launch the Network and Sharing Center by navigating to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
- From the "View your active networks" section, click the hyperlink for the desired network to open the corresponding Connection Status dialog ("Cisco AnyConnect Secure" is selected below).
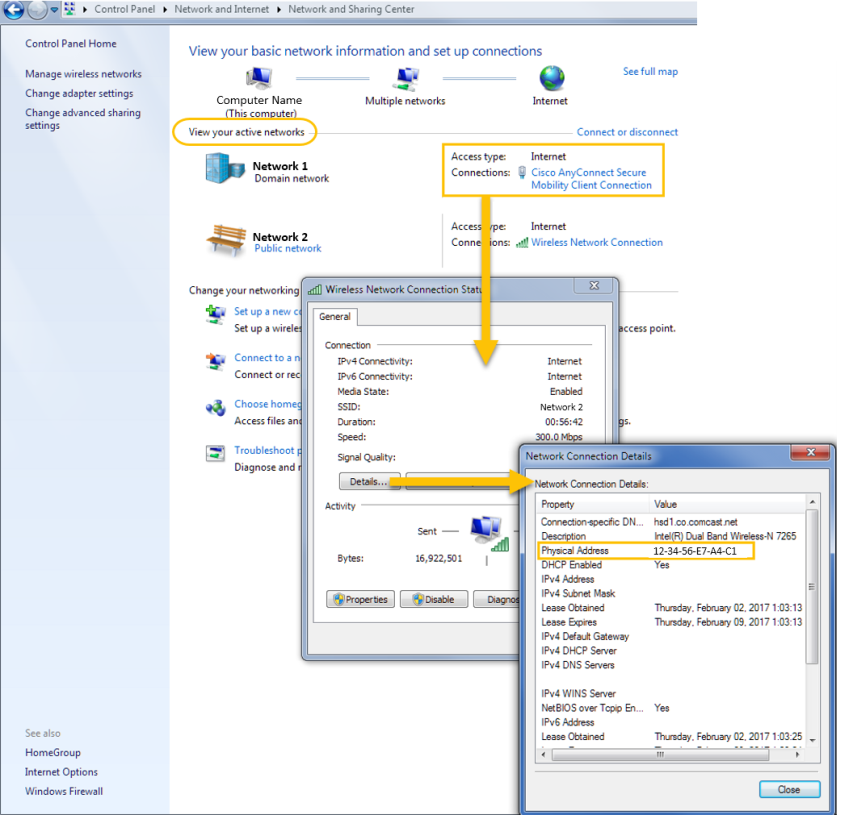
- From the Connection Status dialog, click on the "Details..." button to view your MAC (physical) address, which is a 12-digit hexadecimal number (48 bits in length).
From Windows Command Prompt
- Launch the Command Prompt using the Run window (press Win+R on your keyboard).
- Type cmd or cmd.exe and click OK.
- From the Command Prompt, navigate to the directory where you extracted the LicenseServer.zip file, which contains the FlexNet files required to configure the licensing server. If you haven't already extracted the files to your computer, see Floating License Installation Overview and then continue here.
- From the appropriate directory, type lmutil hostid to view your MAC (physical) address, which is a 12-digit hexadecimal number (48 bits in length). In the example below, the MAC address is underlined in red.
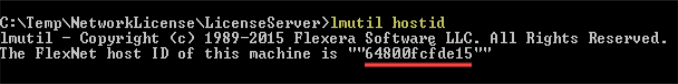
Note: If more than one MAC address is shown, use the address associated with your wired network (LAN interface). Do not use addresses associated with wireless routers, tunnel adapters, virtual adapters, etc.



